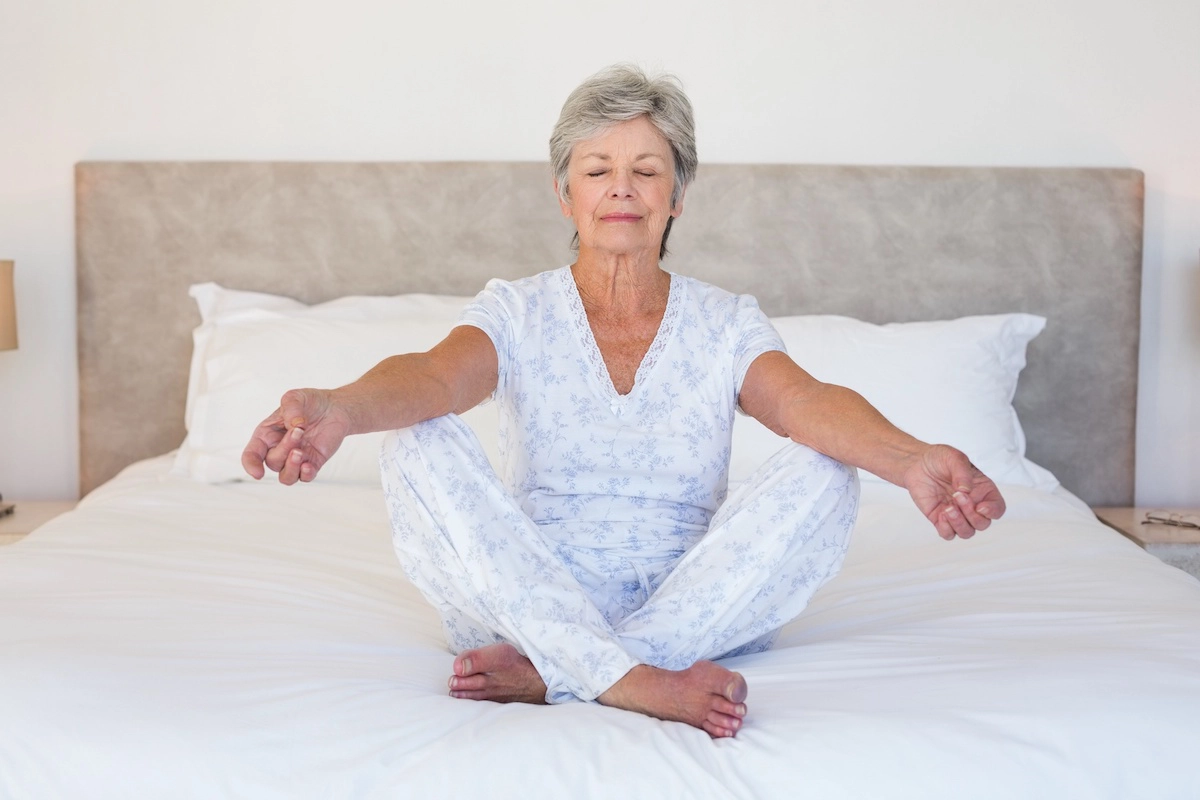
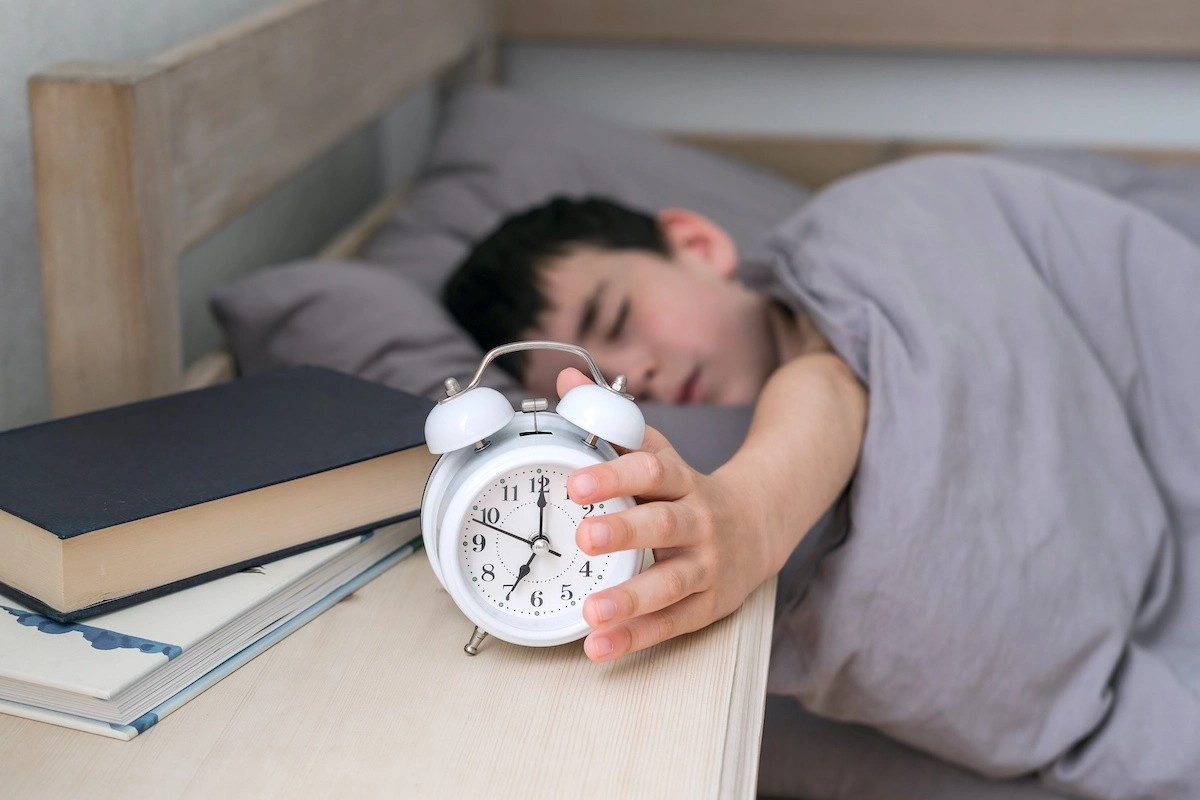
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), there is emerging evidence that meditation may have beneficial health effects. These include potential improvements in stress, anxiety, and depression. Meditation may also improve sleep quality.
There may be several possible benefits to meditating in bed, including:
- Comfort: Meditating in bed helps people feel comfortable and relaxed in a familiar environment.
- Relaxing space: Many people associate their bed with rest and relaxation. This sense of calm may help a person to focus without distractions.
- Convenience: Meditating in bed after waking up or before going to sleep is a convenient way to fit meditation into a person’s day.
- Starting the day positively: Some people may benefit from meditating in bed after waking up. This could help people set their intentions for the day, feel less stressed, and be more positive about the day ahead.
- Sleep: Engaging in meditation at night may improve sleep quality.
A comfortable, calm environment may help people relax and focus on meditating. Although everyone’s idea of an ideal space is different, the following tips might help:
- Make the bed as comfortable as possible.
- Have plants in the bedroom.
- Maintain a clean and tidy space.
- Use soft or warm colors and lighting.
- Avoid using screens before bedtime.
- Keep the room cool.
- Use pleasant fragrances from scented candles and essential oils.
- Stick to a regular sleeping and waking routine.
- Reduce distracting noise.
There is a lack of research into how environments affect meditation. However, quiet and cool environments can improve sleep quality. The same is true of a regular sleep routine.
How to meditate in bed
There are several meditation techniques people can try in bed. Using a meditation app can be useful for learning how to meditate.
Meditation techniques include:
Mindfulness: Mindfulness meditation works to induce a present-focused and nonjudgmental headspace. It encourages people to focus on the breath and sensations in the body. It also involves observing thoughts and feelings without dwelling on them.
Body scan: A body scan meditation works by attending to different body parts, focusing on how they feel. The process is systematic, starting from the top of the head and ending at the tips of the toes.
Progressive muscle relaxation: This technique works by tensing and then relaxing muscle groups. An individual can work through different muscle groups in a sequence, attending to the feeling of relaxation.
Sound meditation: Where an individual focuses on external sounds. These might be nature sounds, chants, or singing bowls. The idea is that a person returns attention to these sounds if their focus starts to drift elsewhere.
Breath awareness: Breath awareness meditation involves paying close attention to the flow of breath. The individual attends to the rhythm, sounds, and physical sensation of the breath.
Loving kindness: It fosters calming feelings of compassion and love toward the self and others. Individuals can do this by repeating positive phrases. They can also imagine making positive statements about themselves and others.
Guided visualization: Guided visualization works by following verbal instructions or by recalling images.
There is no right answer to this question. One argument is that any meditation is better than no meditation. If a person is only able to meditate once a week, this should not be a barrier to trying out the therapy.
People can consider starting with a few mindfulness sessions per week and increasing the frequency if they feel it is necessary. Meditation may also be a tool someone uses on an as-needed basis.
Sources:
- Davis, D. M., et al. (2012). What are the benefits of mindfulness?
http://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/features/pst-48-2-198.pdf - Meditation and mindfulness: What you need to know. (2022).
https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/meditation-and-mindfulness-what-you-need-to-know - Noonan, S. (2014). Mindfulness-based stress reduction.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3894868/