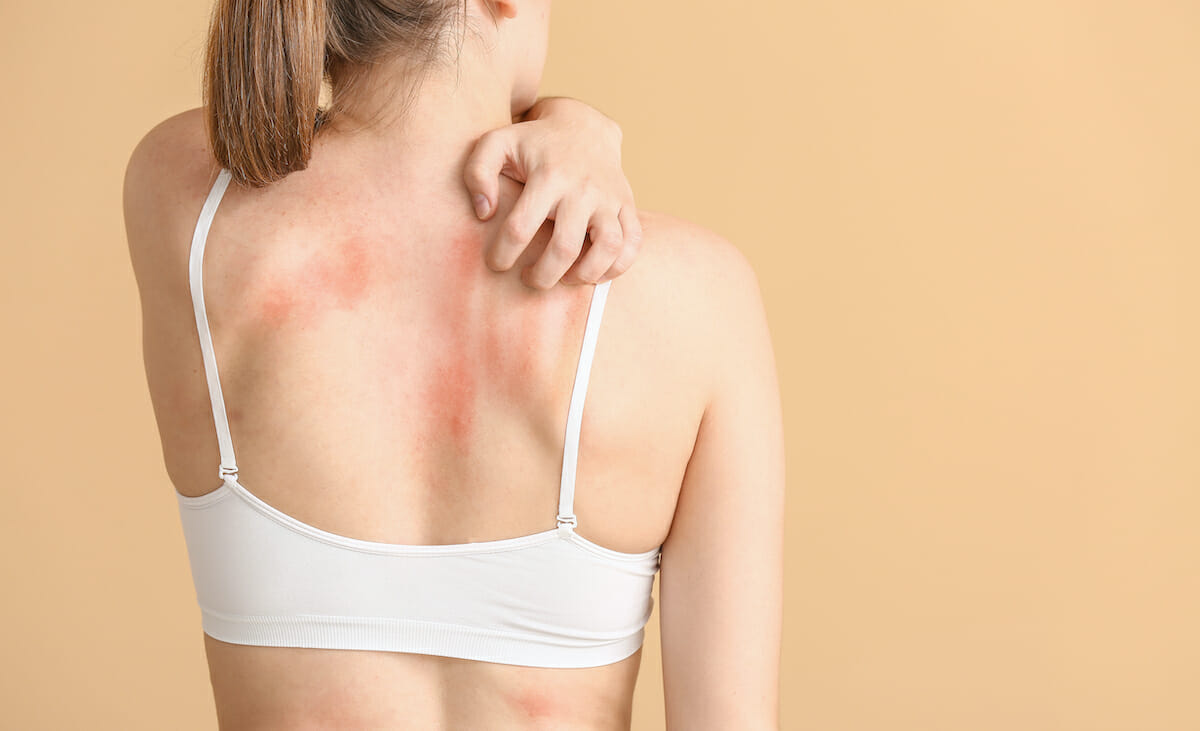
itching after taking a shower. The water from the shower can strip away the skin’s natural oils, causing dryness and itching.
Treating these symptoms may not always be as simple as applying a lotion or moisturizer. Sometimes, dry, sensitive skin needs additional care to alleviate the irritation and dryness that cause the itch.
It is also important to watch for other symptoms, such as peeling, scaling, or rashes, as these may indicate a condition that needs treatment.
Causes of itching after a shower: Many things can cause the skin to feel itchy after taking a shower or bath. Here are some of the most common reasons for itching after a shower:
Dry skin lacks moisture and may feel tight or itchy, especially after a shower. Cleansers, soap, and water can remove the skin’s natural oils that keep it supple and prevent dryness.
When a person takes a hot shower, the soap, and water strip away the skin’s oils, which can cause the skin to feel tight and itchy. In extreme cases, the skin may even crack or bleed.
Prevention: The best way to prevent itchy skin after a shower is to apply moisturizer immediately after towel drying. A heavy moisturizer, such as a cream, oil, or ointment, can help seal in moisture if a person applies it while the skin is still slightly damp.
People with very dry or sensitive skin should read the product label carefully before using a moisturizer. Some products can make itching worse, as they contain irritating ingredients or cause allergic reactions.
In general, avoiding products containing fragrances, menthol, and alcohol is best, as these can cause further dryness, irritation, and itching.
What does seasonal change have to do with it? If the outdoor air is hot and humid, this can result in dry skin that is easily irritated.
People can take steps to prevent or minimize these conditions. These steps include:
washing the body using fresh, clean water and a mild, gentle cleanser or body wash
taking showers and baths in warm water
applying moisturizer after every shower and bath
turning up the thermostat if the air conditioning makes the home too dry
wearing loose-fitting clothes made of cotton
Colder temperatures: Winter rash refers to dehydrated skin that occurs in the colder season. Possible causes include:
colder temperatures
low humidity levels
central heating
Winter rash may cause itching, inflammation, and rough patches on certain body areas. In some cases, it may spread across multiple parts of the body. The most commonly affected areas are the hands and arms, which typically get more exposure to cold temperatures.
The main treatments for winter rash include rehydrating moisturizers, oils, and creams.
As with heat rash treatments, a person should avoid harsh soaps or cleansers and use warm water when washing.
People may also benefit from using a humidifier in their home to counteract the effects of central heating.
Eczema refers to skin inflammation that can lead to itching and excessive dryness. It is a chronic condition that can also cause a rash or bumps on the skin. Eczema may feel even more itchy and uncomfortable after bathing or showering when the skin lacks natural oils. Scented body washes, soaps, and the hot water from the shower may also trigger itching.
People with eczema may need to use hypoallergenic products and apply moisturizer throughout the day. A dermatologist may be able to provide recommendations on which specific products to use.
Reactions to skin care products: Many people enjoy using scented cleansers, soaps, and hair products in the shower. However, these products can trigger allergic reactions in some people, leading to itching and other symptoms. This is known as contact dermatitis.
The National Eczema Association explains that fragrance is one of the ingredients most likely to cause a skin reaction.
If someone finds that moisturizing alone does not relieve itching, they may need to switch shower products. They can try using only fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers and see whether the itching goes away.
Reaction to laundry products: Scented laundry products could also lead to post-shower itching, especially if someone uses scented products on their towels. Toweling off after bathing could transfer some of the fragrances from a laundry soap or fabric softener to the skin. This can lead to itching and irritation if a person has an allergy or sensitivity to the product.
People with sensitive or itchy skin may wish to avoid using laundry products that contain fragrance or dye to wash their towels or clothes.
Treatment and remedies
People who notice itching after taking a shower may find relief by following these steps:
Keeping showers as short and cool as possible: Using cooler water for shorter periods can help avoid stripping the skin of its natural protective oils.
Shower no more than once daily: More showers mean more chances to strip the skin’s natural oils. According to the American Academy of Dermatology Association, children may be able to shower less frequently than adults—about once or twice per week.
Avoiding long, hot baths: These can dry the skin. A person can also consider adding colloidal oatmeal or bath oils when taking a bath to help moisturize the skin.
Refraining from scratching the skin: Scratching the skin can irritate and injure it, making the itching worse.
Avoiding using washcloths, scrubs, or harsh sponges: These may irritate the skin in the same way as scratching.
Using fragrance-free moisturizing cleansers or soaps: People can look for hypoallergenic products or those suitable for eczema and sensitive skin.
Drying the skin by patting it gently: It is important not to rub the skin with a towel, as this can cause irritation and remove the skin’s natural oils.
Applying a heavy, fragrance-free moisturizer or ointment: It is best to do this immediately after patting the skin dry.
Avoiding applying large amounts of lathering soaps or cleansers: Lathering agents can worsen dry skin, and they are not necessary for cleaning the skin effectively.
Using a humidifier: This can be especially helpful in dry climates or throughout the winter months. Low humidity can exacerbate dry skin.
Avoiding fragrances in laundry detergent and fabric softener: These ingredients may get on towels and clothing and cause itching after a shower.
Avoiding using products that contain retinoids: Retinoids regulate epithelial cell growth, but they can be an irritant and worsen dry skin. Unless a doctor has prescribed them, people should avoid using retinoids. Retinoids include:
Limiting or excluding products that contain alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA): AHA is an ingredient that may cause burning or itching on dry or sensitive skin.
When to consult a doctor
Usually, a person can treat mild itching after taking a shower by following the steps above and taking care to keep the skin moisturized.
In some cases, however, itching is not related to the skin itself. A health condition such as nerve damage or multiple sclerosis may cause the nerves in the skin to be overactive. This can cause itching without a rash or another obvious cause.
Itching from nerve-related health conditions may lead to excessive scratching, which can irritate the skin and make itching worse. It may also cause minor wounds that make an infection possible.
Sometimes, a mental health condition can cause a person to scratch their skin excessively. Some mental health conditions that may cause this include:
depression
anxiety
obsessive-compulsive disorder
excoriation, a skin-picking disorder
If a person suspects that they have a nerve-related or mental health condition, they should speak with a medical professional.
Summary
Most people will be able to treat post-shower itching by using moisturizers, lotions, and other home remedies. However, if the itching persists after trying these remedies, a person may wish to speak with a healthcare professional to rule out other, more serious health conditions.
Source: Adapted from the article https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326974