Special to The Island News
Though present in men and women, testosterone is a primary male sex hormone that helps men produce sperm and red blood cells, achieve erections and develop strong bones and muscles.
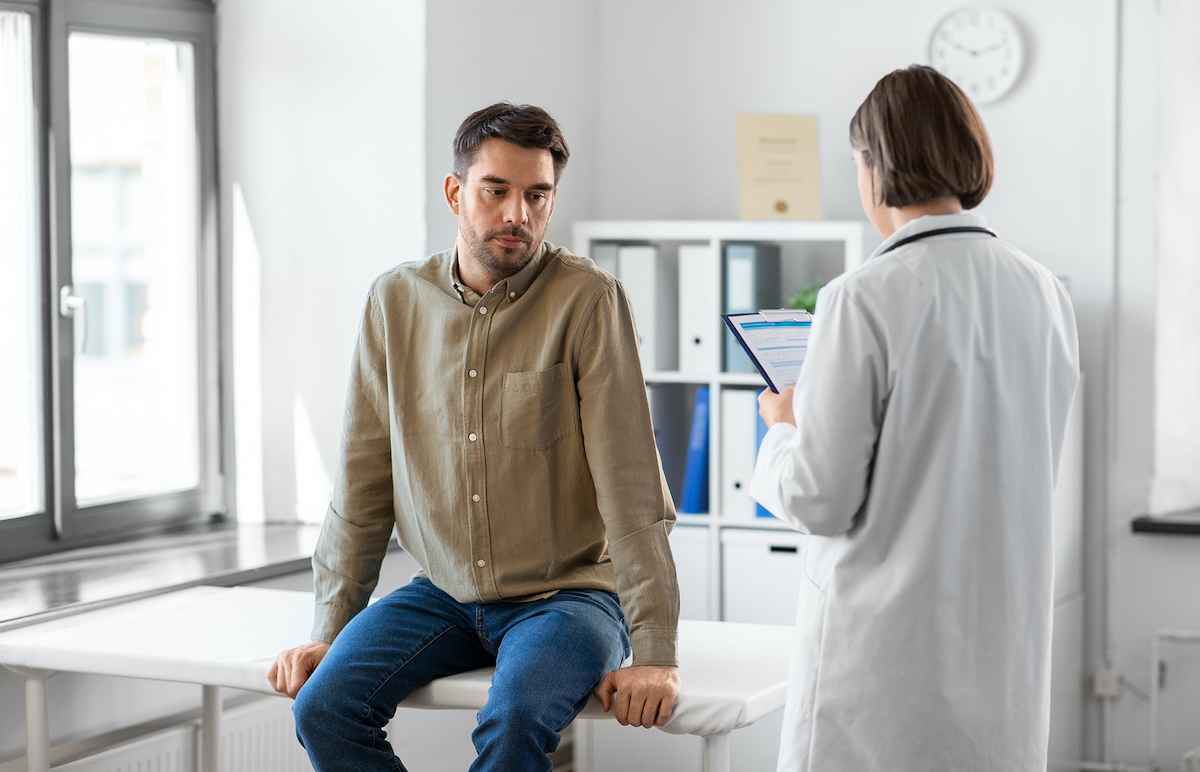
Over time, however, testosterone levels drop. If the level goes too low, you may experience low testosterone symptoms.
“Unfortunately, these symptoms often get overlooked because they’re similar to those produced by other conditions,” says Matthew Baker, PharmD, PA-C, certified physician assistant and pharmacist with Beaufort Memorial Urology Specialists. “Recognizing early signs and seeking medical care can help you regain lost benefits of testosterone.”
Low testosterone and sexual health
When your testosterone levels drop, you may experience sexual signs of low testosterone, including:
- Declining sex drive — Baker says it’s normal to lose some interest in sex as you age, but “low testosterone can cause you to lose sexual desire altogether.”
- Erectile dysfunction — According to the Urology Care Foundation, most men have a hard time achieving erection on occasion. Frequent erection issues should be evaluated, as they may result from low testosterone.
- Low sperm count — Some men never realize they have a low sperm count. It’s normally noticed after a year of unsuccessful attempts at impregnating a female partner and subsequent testing.
Physical health changes
Your body changes throughout life, and low testosterone can result in physical symptoms you may think are just part of getting older. Living with the condition may cause the following physical symptoms:
- Bone loss — Because your body needs testosterone to maintain bone strength, bone loss is common when you lack testosterone.
- Muscle loss — Sarcopenia is age-related loss of muscle mass, physical performance and strength. Since testosterone helps build muscle, your risk for sarcopenia increases if you have Low T.
- Sleep issues — Low testosterone can cause insomnia and other sleep difficulties. The relationship also works the other way, as poor sleep can lower your testosterone level.
- Weight gain — Lose testosterone, and you may gain weight. In fact, a lack of testosterone increases your risk for obesity.
Evaluating low testosterone symptoms
Because low testosterone affects every man differently and symptoms overlap with other conditions, diagnosing Low T can take time. Detection often involves the following:
- Physical evaluation — During a full physical exam, your primary care provider reviews your medical history and examines your body for abnormalities. You also discuss any potential low testosterone symptoms affecting you.
- Testosterone blood tests — In-office blood tests provide an easy way to check your testosterone level. Your test should take place in the morning, when testosterone levels are highest. The blood draw takes only a few minutes, and results help determine if your symptoms are linked to testosterone levels. Eating and drinking can affect the results, so ask your care provider whether you should fast prior to your exam.
- Other tests — Based on your symptoms and other test results, additional testing can help better understand your condition and rule out other conditions. You may undergo an imaging scan to measure bone density, hormone tests to check your sperm-making ability and more.
Treating low testosterone symptoms
When a drop in testosterone is related to aging, testosterone replacement may help. Replacement therapy is not appropriate, however, if you have certain conditions, such as enlarged prostate or prostate cancer.
Low testosterone connected to an underlying health issue requires different treatment. This may include one or more of the following:
- Healthy lifestyle — A healthy diet and regular exercise improve every area of health. The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs recommends aerobic and strength-training exercises to boost testosterone production.
- Medical management — Your testosterone may drop if you have uncontrolled Type 2 diabetes or other health issues. Managing chronic conditions may increase your testosterone level.
- Weight loss — Being overweight can lower testosterone. Obtaining and maintaining a healthy weight may raise your testosterone.
“Once we identify the presence and source of Low T, a customized treatment plan gives men back their lives,” says Baker. “But the first step is noticing symptoms and speaking up. You have to advocate for your health.”